By Airon Rodrigues
AMP, also known as Accelerated Mobile Pages, is a project by Google project with one aim; to speed up the delivery of content using stripped down codes known as AMP HTML. The AMP Project was announced by Google on October 7, 2015, and was first exposed to web users in February 2016.
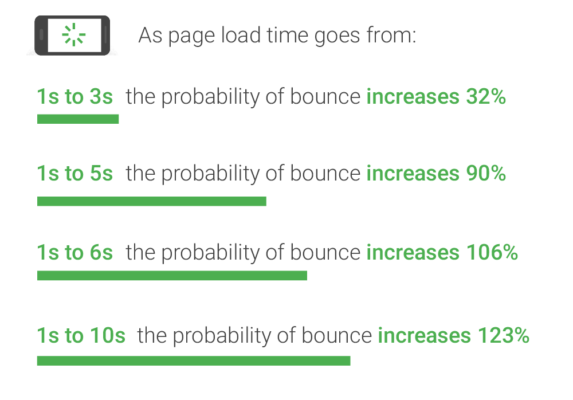
The purpose of AMP is to present a web page to a user as quickly as possible. Page speed, as we know, is a ranking factor.
Essentially, Page speed is an important factor for ranking in Google search results. Load time affects not only visitor engagement, retention, and conversion rates, but it can also affect a website ranking.
Faster loading websites result in satisfied users who are likely to leave with a positive experience and return to the site in the future. However, faster sites don’t just improve user experience; they can also improve conversation rates.
A website that is quicker to load a certain product will have a better chance of converting a lead compared to a website who makes a user wait when (trying) to purchase a product online.
What is AMP?
AMP is a project designed by Google as an open source coding standard for publishers. The aim of AMP is to make static content load instantly, which makes it highly suitable for publishers.
Essentially, AMP is a stripped-down version, or alternate version, of a mobile site that conforms to the specifications published by the AMP project. This alternate website runs on a reinvented version of HTML, which is known as AMP HTML.
AMP HTML strips out most of the elements which cause a slow page speed such as JavaScript, third-party scripts, and CSS.
Why Is It Important?
According to Google, a page created with AMP HTML can load anywhere from 15 to 85% faster than the non-AMP version of that page.
AMP is important because it provides a user-friendly experience, something that Google highly values. If users are coming to a site primarily to read content from a blog or news section, AMP will carry the heavy lifting to help load the content instantly.
A good example is to imagine there are 3 different sites serving 3 how-to guides on the same topic. If only one of these sites has AMP, it would be the clear winner in providing useful content in the fastest manner possible, therefore resulting in a good user experience.
In addition, AMPs websites load faster which means it will decrease bounce rate and help increase the number of visitors to a website.
Again, Google is all about user experience. It favors websites that can provide a good user experience. One way to do this is through Page Speed. Considering AMP will help boost page speed and it can also help to increase Google rankings.
The below images display the AMP version of a Guardian news article (left) vs. the regular mobile version (right). As seen in the AMP Version, the content underneath the image has already loaded whereas the mobile version does not display this content.
Are There Limitations to AMP?
Because AMP HTML is designed to strip away certain elements that slow down a website, there are certain limitations to consider before implementation.
Some of the visual limitations are as follows:
- No JavaScript will be allowed other than an off-the-shelf AMP library
- Images will only load when you scroll down to them (lazy load functionality)
- A streamlined version of your CSS will be required
You can read more about the technical requirements for AMP HTML here.
What Sites Benefit From AMP?
Essentially, not all websites will benefit because keep in mind, AMP strips away certain visual elements from a web page to increase page speed.
For eCommerce websites that heavily rely on product visuals, AMP would not necessarily help the situation. Sites that will benefit from AMP are publishing sites. Sites that display and produce content. What about websites that have a blog or news section but aren’t necessarily publishing sites?
The key here is to not apply the entire site to AMP, but rather only transition the blog, news, and updates section into AMP.
Do You Need To Use AMP?
For those who are already taking manual steps to increase the speed of a website, it may not be necessary.
However, if a website is struggling to achieve a quicker page speed to the point where Google rankings are suffering, it may be time to consider installing Google AMP.